Immersive Learning – Instructional Strategies to Make it a Reality
This blog discusses what immersive learning is and four instructional strategies to create immersive learning environments.
Immersive learning is a term being discussed by e-learning professionals in the past few years, but you may be surprised to know the style has been our natural way of learning since ages. It is basically learning through experiences. So how did this age-old method enter the e-learning space?
E-learning professionals have discovered learning can be enhanced by ‘immersing’ learners in a self-contained, simulated environment; helping them learn by experiencing. This has become a possibility with advances in technology and developments in the digital space.
Immersive e-learning environments or ILEs can be used for training in a number of areas. They:
- Create rich and complex content-based learning where learners can improve their technical, creative, and problem-solving skills
- Engage learners and help them apply the skills to their work
Immersive training techniques increase relevance, engage learners, and can be used to train employees in critical areas by creating relevant scenarios. Areas of training include those with:
- Maximum repercussions when training is not adequate (such as health & safety and compliance training)
- Costly and dangerous to create environments
Let’s now look at four instructional strategies that help develop immersive learning:
Storytelling:
The content is presented in the form of a story to engage learners and help them understand better.
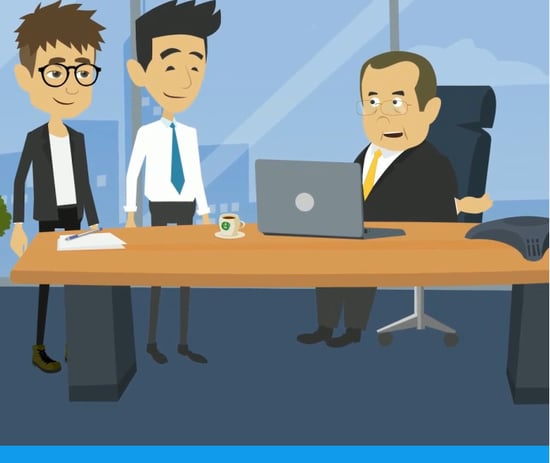

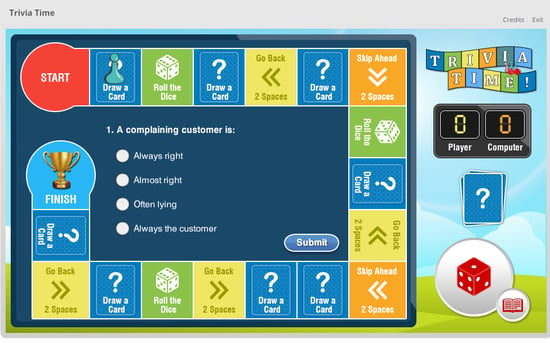
This screenshot is from a course where scenarios were used to explain how to schedule a meeting in MS Outlook.
Stories help learners by:
- Demonstrating how they should act in a particular situation
- Making it easier to understand abstract concepts through anecdotes and analogies
- Offering visual metaphors, a powerful tool to help people learn
Gamification:
This is the use of game elements and game mechanics in non-game contexts to engage learners in solving problems and motivating them to learn. It offers immersive learning through the use of genuine contexts, activities, and assessments.
For example, a course to teach employees customer relations is made engaging when employees play a game where they learn to identify customer problems.
Simulations:
These are used to incorporate the concept of ‘learning by doing’ and offer experiential learning. Simulations can be used for diverse learning needs such as ERP training, process training etc. For example, end-users were trained on Workday, a HRIS application, through simulations which demonstrated how the software actually works.
Augmented Reality:
In augmented reality, the physical, real-world environment is augmented with computer-generated graphics, texts, sound, and videos to enhance learning. It therefore offers rich contextual learning.
Training happens in a safe environment where learners can control their learning and manipulate objects.
Some examples of AR training:
- Healthcare professionals can use the augmented environment to practice complex surgeries without risks.
- Employees can be trained on operating heavy equipment and firefighting.
- Sales reps can be trained on interacting with customers.
Check out this video:
Are you using immersive instructional strategies to increase relevance, engage the learner, and provide opportunities to practice what they are learning? What strategies have you used? We would love to hear from you.