4 Benefits of AI for Learners… and Teachers
KnowledgeOne
APRIL 3, 2024
This is the case, for example, with the correction of objective answers in exams, or the creation of formative tests and quizzes. Feedback, therefore, has not only an informative but also a motivational role. Artificial intelligence can… Save teachers’ time.




















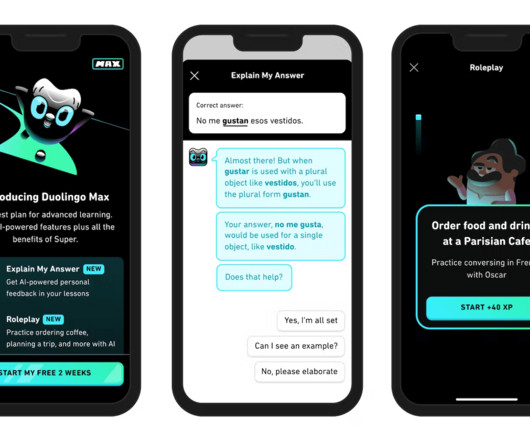












Let's personalize your content