An eLearning project is a unique challenge, with myriad details and moving parts. Keeping the project running to time and meeting everyone’s expectations requires skilful navigation through potential pitfalls that can be as painful for eLearning creators as they are for stakeholders.
The good news is that a well-structured Design Specification Brief will facilitate communication, clarify ambiguities about the content or process, and outline an efficient, effective way of working.
The key elements outlined below, together with the supporting questions, will help you to structure the information and assets you already have, as well as identifying any gaps where further research, communication or curation is required. Collaborating with others to fill these gaps (stakeholders, colleagues, writers, designers, developers, Subject Matter Experts (SMEs), agencies and anyone else who will be involved in the project) will assure integrity and promote a sense of ownership among everyone involved.
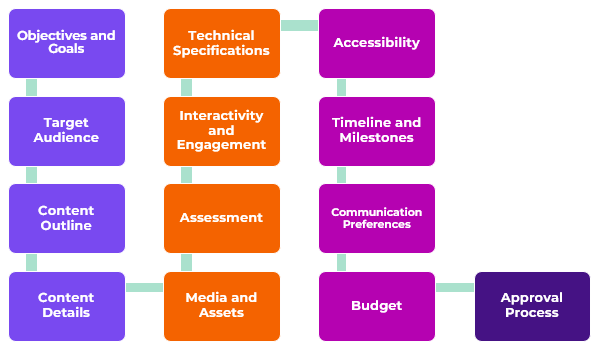
objectives and goals:
-
What will the learners do better after completing the intervention?
-
What are the problems that the learning should solve?
-
How will the learning align with organizational and personal development goals?
Clearly outline the primary learning objectives and the desired outcomes of the eLearning. This provides the writers and developers with a clear understanding of what the intervention aims to achieve.
target audiences:
-
What do you know about the learners?
-
Is the learning aimed at specific roles or departments, or a broader audience?
Describe the characteristics of the learners, including their prior knowledge and experience, skill levels, and any specific learning needs. Consider whether information such as age, background, personality type or learning preferences could be helpful. Include any insights about the organizational culture that might be relevant. Also, what is their motivation to complete the eLearning? This information helps the writers and developers tailor the content and approach to the audience.
Content outline:
-
What are the topics or chapters that should be covered?
Provide an overview of the topics, modules, or chapters that the intervention should cover. A hierarchical structure of the content will help the writers and developers organize the module effectively.
content details:
-
What key points and concepts must be included?
-
Is there any ambiguity in the terminology used?
For each topic or chapter include key learning points, important concepts, and relevant examples including case studies, models, and theories. Remember that Instructional Designers and Digital Developers are unlikely to be experts in the subject matter, so share any existing resources, including media and documents, that they can use to understand the subject matter better. Consider including a glossary of any terminology or acronyms used.
media and assets:
-
What images, videos, animations, or audio clips can be included?
Indicate the preferred multimedia elements to be used. If any specific branding guidelines or design elements are required, provide those as well.
assessment and evaluation:
-
How can we prove the learner has met the objectives?
Explain how the learners' understanding and progress will be assessed. Include details about quizzes, scenarios, or assessments that need to be integrated into the module.
interactivity and engagement:
-
Are there any specific interactions you would like to see?
-
What real-world tasks could be represented by interactions?
Describe the level of interactivity expected in the module. If any gamification elements are to be included fully explain the requirement, as an interactive scenario would be costed very differently to, say, a visual scoring system.
technical specifications:
-
What Learning Management System (LMS) will host the learning
-
Do the modules need to be available offline?
-
How will the modules be accessed?
Provide as much information about LMS as you can, including acceptable interoperability standards such as SCORM/AICC etc. Also, specify any technical constraints or requirements that the developer should consider during the development process, for example file size, or whether the learners will be using laptops, tablets, or smartphones.
accessibility:
-
Are there any considerations to make the content inclusive and accessible to all learners?
If the eLearning needs to be accessible to learners with disabilities, provide guidelines for making the content inclusive, such as ensuring screen-reader compatibility and keyboard navigation.
timeline and milestones:
-
When will the project need to be completed?
-
When will the storyboards, builds, and reviews take place?
Set clear deadlines for the different stages of development, including content creation, reviews, and final delivery. Agree on the milestones that the project team will use to track progress.
communication preferences:
-
Do you prefer Teams chats or formal emails?
-
How regularly would you like to be updated?
Establish a communication protocol, including preferred channels for feedback, regular check-ins, and how to address potential questions or concerns during the development process.
budget and resources:
-
Is the budget fixed or flexible?
-
How much time will you and other stakeholders be able to contribute?
-
Has the cost of media, such as stock imagery or voiceovers, been accounted for?
If there are any budget constraints or resource limitations, communicate them to the writers and developers so they can plan accordingly.
approval process:
-
Will one person oversee coordinating multiple stakeholders during review stages?
-
Will senior managers need to provide their approval?
Define the process for review, feedback, and approval of the eLearning content. Identify key stakeholders who will be involved in the approval process.
This process is not exhaustive, but it should provide a useful starting point for considering the many factors that will contribute to a successful eLearning project. There may be parts of this template that you choose not to include, as they may not be relevant for your project. Also, if there are any other factors not outlined here that you think should be included in the perfect Design Specification Brief, let us know in the comments below. After all, information gathering, communication and collaboration are the key themes for creating the perfect plan and the perfect eLearning project.
Talk to us today if you would like to find out how we can help you with your L&D offering!






Is this article interesting?