Motivation is the force that drives human behavior. It is the process through which humans initiate and maintain behaviors that lead to the achievement of certain goals. Motivation is a complex psychological process that is influenced by individual, environmental, as well as external factors. Motivation plays a role in every aspect of our lives and is a crucial predictor of learning success and learning outcomes. This article will look at three theories of motivation and how they impact eLearning. You will also find tips to increase learner motivation using the theories of motivation mentioned here.
3 Theories of Motivation to Boost eLearning Courses
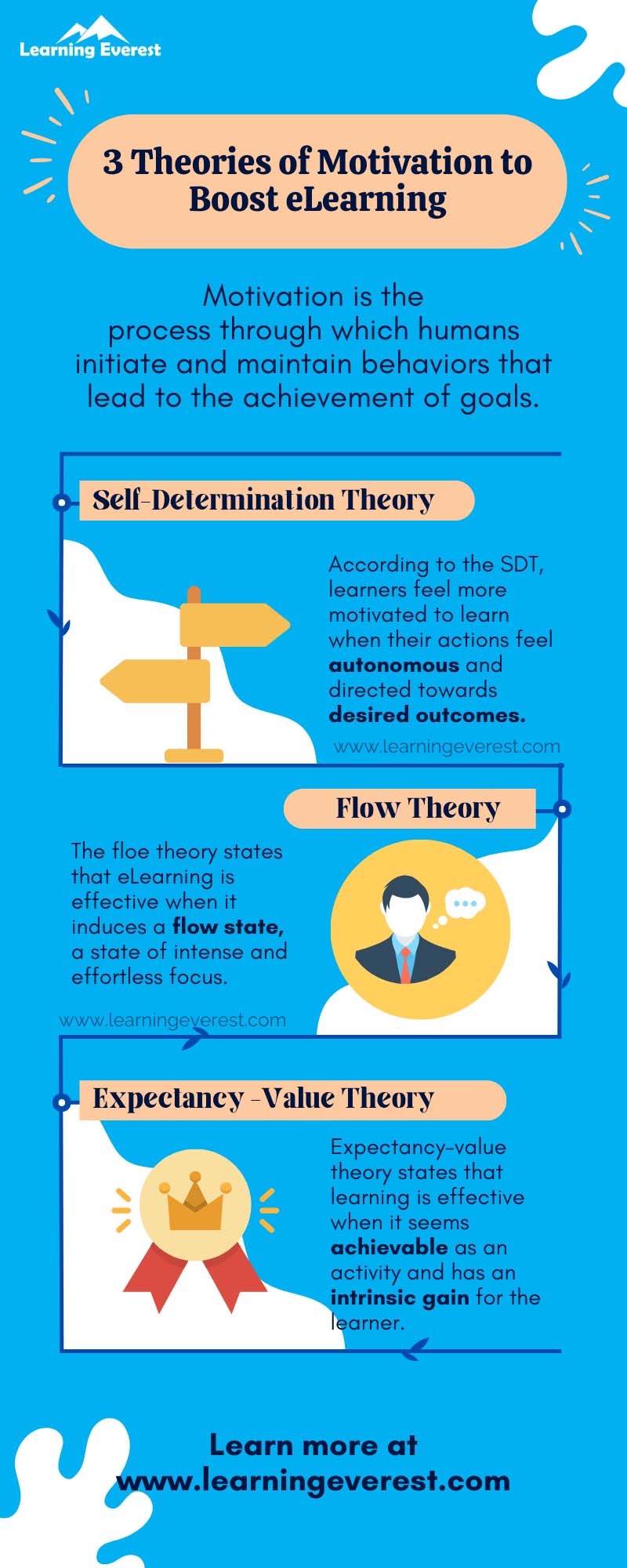
Theory of Motivation #1: Self-Determination Theory
The self-determination theory (SDT) is a popular theory of motivation that can be applied to all aspects of human life.
As the name suggests, the theory places emphasis on humans’ ability to make choices about their lives. According to the SDT, humans are more likely to feel motivated and take action when they feel their actions are autonomous and will lead to desired outcomes.
In order to feel self-determined, there are certain psychological components that an individual must feel. They are:
- Autonomy – People must feel in control of their behaviors. Individuals feel more motivated when they have the freedom to determine their behaviors by making choices.
- Competence – People must feel equipped and able to carry out tasks. This is also referred to as a feeling of mastery over the actions they must perform. Although competence influences motivation, people must also learn, feel challenged, and receive feedback to cultivate competence.
- Relatedness – Also referred to as connection, this component refers to an inherent desire to feel connected or attached to others.
These components lead to intrinsic motivation, which is motivation that emerges from internal needs and drives.
However, intrinsic motivation often cannot operate in a vacuum without social support and positive feedback.
In the context of learning, the SDT holds that self-determined learning stemming from intrinsic motivational factors like accomplishment, passion, desire for knowledge, etc., is more impactful and effective. However, most learners don’t find the act of studying intrinsically interesting.
Thus, in learning, the application of the SDT needs to be supplemented with not only social support and positive feedback, but forms of extrinsic motivation that can synergize with an individual’s desire for self-determination.
This kind of motivation can be divided into three categories:
- Introjected motivation – Things individuals do to avoid feelings of guilt and maintain self-worth.
- Identified motivation – Motivation that stems from an individual perceiving a behavior as personally relevant and beneficial.
- Integrated motivation – Motivation that occurs when an individual perceives the value of an activity as tied to a part of their self.
Integrating Self-Determination Theory of Motivation into eLearning
As mentioned above, the best way to integrate the self-determination theory of motivation into eLearning is by emphasizing the personal relevance of engaging in a learning activity.
- Sources of introjected motivation could be scores, grades, ranks, etc. However, introjected motivation is the least autonomous. Hence, it should be used sparingly.
- Sources of identified motivation are:
- Well-written learning objectives that delineate clear and explicit learning outcomes
- Personalized learning pathways
- Scenarios and simulations that directly reflect learners’ context
- Open access eLearning libraries housed on an internal LMS
- Integrated motivation can be created by
- Providing learners with specific and technical courses that are from their specialty/role/niche. For instance, a course on a new technology for you’re the IT team
- Allowing for personalized avatars in courses
- Providing certificates and tangible career advancement upon course completion
- Additionally, provide ample learner feedback through correct/incorrect feedback, message boards, instructor videos, and opportunities to retry/retake sections
Theory of Motivation #2: Flow Theory
The flow theory talks about a state of intense focus in which an individual is completely engaged and immersed in an activity. It is a positive and pleasurable state of mind, which people colloquially refer to as “getting in the zone.” This state of deep concentration is called a “flow state.”
A flow state is characterized by the following:
- Effortless sustained attention
- Greatly reduced distractibility
- Heightened senses and cognition
- Fluid thinking with easy information processing and seamless connection between ideas
- Increased creativity
- Improved knowledge acquisition and retention
In eLearning, the trick to eliciting a flow state in learners is to engage them and remove all potential cognitive and emotional barriers a learning experience might have. This can be achieved by getting creative with learning solutions and deliberate, goal-oriented instructional design.
Applying the Flow Theory of Motivation to eLearning Courses
Here are some strategies to make it easier for your learners to get into a flow state while learning:
- Start strong – Start with a catchy opening, be it through a video, striking visuals and graphic design, witty text, or an interesting and interactive menu with animated elements. Set an interesting tone for the course right at the beginning to grab the learners’ attention.
- Structure the course strategically – Avoid jumping into a course without proper context setting. This can be done in many different ways, for example:
- Giving a quick pre-test or quiz before starting
- Letting learners ponder over a thought-provoking question that ties into the course content
- Giving a recap of past modules or lessons to help learners connect with course content
- Progressing from core concepts to more advanced ones
- Make it consistent – The learning experience should have a consistent “look and feel” and functions. Place similar buttons in similar places, keep colors of triggers consistent, use an eLearning template to design your course, and establish patterns in the course’s user experience to make navigation easier.
- Use gamification, scenario-based learning, and simulation-based learning – These techniques are some of the most engaging formats of eLearning being used at present. They incorporate interactive elements into courses and promote learner choice, immersion, and meeting goals.
Theory of Motivation #3: Expectancy-Value Theory
The expectancy-value theory of motivation states that people engage in behaviors when the outcome is favorable and attractive to them.
This theory has two components, namely – expectancy for success and task value.
- Expectancy for success – Expectancy for success refers to a person’s beliefs about their likelihood at succeeding at a task and achieving the favorable outcome.
- Task value – Task value is the intrinsic gain that an individual will receive upon performing a behavior, such as utility.
Hence, people make decisions about whether they want to begin and continue a behavior based on these judgements about the task’s expectancy for success and task value.
In eLearning, the expectancy-value axis can be leveraged to amplify aspects of a course that caters to these components.
For instance, a course’s expectancy for success can be increased by making shorter courses, providing tangible rewards, and clearly outlining the professional outcomes of the course.
Similarly, a course’s task value can be enhanced by making it more enjoyable and engaging, linking courses with learners’ future goals, and waiving off certain costs that come with learning on the job, such as giving paid time off or learning days.
Conclusion
When building eLearning courses, instructional designers should not only focus on course content and visual design, but also add elements that capture aspects that motivate their target learners. Planning ahead by conducting a thorough needs analysis is a crucial step for creating impactful and motivating courses.
Infographic
3 Theories of Motivation to Boost eLearning Courses – Infographic
Knowledge check!
References
Park, S. (2018). Motivation Theories and Instructional Design. In R. E. West (Ed.), Foundations of Learning and Instructional Design Technology. BYU Open Learning Network. https://open.byu.edu/lidtfoundations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is self-determination theory in eLearning?
According to the self-determination theory of motivation, in eLearning, learners should feel a sense of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in a learning experience, and receive ample feedback and some strategic extrinsic motivators.
What is flow theory in eLearning?
According to the flow theory of motivation, eLearning experiences should be designed to put learners into a “flow state”, i.e., a state of deep concentration and immersion.
What is expectancy-value theory in eLearning?
According to the expectancy-value theory of motivation, learners should be able to see themselves successfully achieving the end goal of a course, and be able to find an intrinsic gain in taking the course.





