Employees taking leave is such a common and expected part of running a business that it can be easy to forget that there are business impacts. The truth is that workplace absenteeism—particularly when it’s frequent or unexcused—can have a significant impact on an organisations’ bottom line.
What is cost of absenteeism?
Absenteeism refers to habitual absences of employees from work. This isn’t the same as occasional sick leave or scheduled holidays—it’s the repeated unexplained and unplanned absence of employees that affects the day-to-day operations of the business. Unmitigated, absenteeism can be costly to organisations and their workforce financially and in terms of productivity and employee morale.
What factors affect cost of absenteeism?
First, let’s clarify the difference between planned and unplanned absences.
- Planned absences include approved leave, such as for personal days or annual, maternity, or paternity leave. These absences are usually scheduled days, weeks, or even months in advance, so organisations are aware and able to prepare.
- Unplanned absences is unexpected leave. This can be due to illness, emergencies, other unforeseen circumstances, or some deeper underlying issues. (We’ll get into those soon.)
Since they’re scheduled, planned absences are easier for businesses to manage and ensure that there’s as minimal a hit to productivity as possible. This isn’t to say that planned absences are entirely without ramifications for organisations, because they still contribute to absenteeism costs. (A day off work is still a day off work, even when accounted for.)
This also isn’t to say that unplanned absences are always unexcused absences with no good reason. Family emergencies, sick days and medical appointments are legitimate and largely unavoidable reasons for unplanned leave, but other reasons like stress or burnout could indicate issues with the workplace that need to be addressed.
Like planned absenteeism, unplanned absences add to absenteeism costs. The extent of those costs depends on the length and frequency of absences.
- Chronic absenteeism refers to frequent absence from work, often for extended periods of time.
- Intermittent absenteeism is when employees are only occasionally absent from work.
Both types of absenteeism can occur for legitimate or illegitimate reasons, and affect the cost of absenteeism. In some ways, intermittent absenteeism is more disruptive to productivity than chronic, as organisations can hire temporary workers to fill positions during extended periods of leave. While neither type is considered to be specifically planned or unplanned, they can be considered an excused or unexcused absence.
Common reasons for absences and what that means for cost of absenteeism
Businesses shouldn’t lump planned and unplanned absenteeism together, because the underlying causes of each require different approaches to solve. The most commonly reported reasons for absenteeism are:
- Family responsibilities or emergencies
- Illness
- Holidays or vacations
- Burnout
- Stress
- Poor morale
- Harassment or workplace bullying
- Mental health
- Injury
- Job-hunting
- Disengagement.
The type of industry or job role will also affect absence rates. Healthcare and other service operations tend to have a higher sickness absence rate than other industries, meaning those services will have increased absenteeism costs as a result.
Time of year also plays a part. People tend to take more time off around public holidays, or take sick leave during cold and flu season.
The organisational impacts of employee absenteeism
So what is the cost of absenteeism, exactly? Put simply, it’s the monetary impact absent employees have on your business operations and revenue. There are a few different ways to calculate an organisation’s cost of absenteeism.
The simple formula (if you only want a rough approximation of the cost of absenteeism), is to double the daily wage of the absent employee.
The more complicated way is to use Houtzager’s formula, which takes multiple different costs into account:
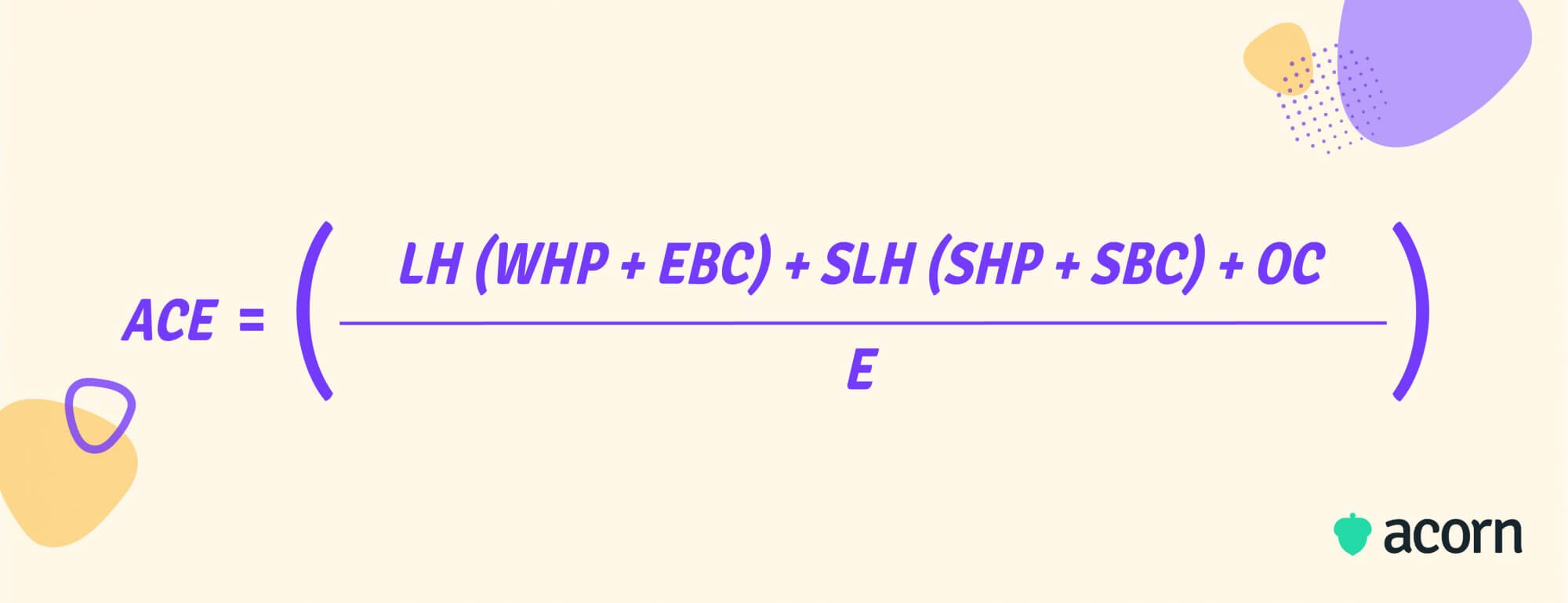
Where:
- ACE is the total cost of absenteeism per employee
- LH is the total number of employee hours lost due to absenteeism in the time period
- WHP is the weighted average hourly pay for employees
- EBC is the cost of employee benefits per hour, per employee
- SLH is the total number of hours supervisors lost due to dealing with absenteeism
- SHP is the average hourly pay for supervisors
- SBC is the cost of supervisor benefits per hour, per supervisor
- OC is an estimation of other, indirect costs
- E is the total number of employees in the company.
So, what expenses contribute to the cost of absenteeism?
There are both direct and indirect expenses that contribute to the total cost of absenteeism. Direct costs are the expenses an organisation incurs due to employee absences. These could include:
- Time off. Businesses have to pay employees for time off, providing paid sick leave, personal leave, and annual leave.
- Overtime and replacements. If an absent employee’s work needs to be covered, businesses may have to provide overtime pay to remaining employees so they can take the work on themselves, or hire temporary staff.
- Reduced revenue. Frequently absent employees disrupt the work process, causing lost productivity, reduced quality of work and less output.
Indirect costs, on the other hand, are intangible costs of absenteeism. These costs include:
- Low workplace morale. When employees have to cover for absent colleagues, it can breed resentment, burnout, or stress, leading to disengagement and low team morale. That impacts the workforce’s ability to be productive and provide services to customers and clients, which will ultimately cost you in revenue.
- Increased turnover. When employees start to feel the bite of frequent absenteeism, they may look for employment at a company that experiences less of it. This will inevitably drive up costs for businesses in recruitment, hiring and onboarding.
- Decreased reputation. The poor workplace environment created by frequent absenteeism won’t exist within a vacuum. Organisations may gain a reputation as a bad employer due to increased absences, which can impact their ability to attract and retain talent.
The cost of absenteeism will differ depending on which direct and indirect expenses are involved, which is why it’s important to understand the underlying issues that cause absenteeism. Employees taking sick days or holidays is inevitable and to be expected, but when they take time off due to stress or burnout, it points to problems in the workplace that need to be identified and addressed.
How do you track absenteeism costs?
So, how do you keep track the costs of absenteeism when indirect costs like reduced productivity are hard to benchmark?
- Know your absenteeism rate. This is the percentage of unscheduled absenteeism among employees. You can find it by dividing the total number of days employees missed by the total number of scheduled workdays (i.e. excluding weekends and public holidays).
- Track direct costs. This includes wages paid to absent employees, temporary staff and overtime workers as well as any other costs that may have come up as a result of absenteeism (like insurance).
- Determine indirect costs. Because these are the intangible expenses to a business, they are harder to calculate. You can get a rough estimate of indirect costs by multiplying the absenteeism rate by the average revenue per employee per day.
Look to your HR software to automate tracking of absenteeism rates and the corresponding costs, saving up time for analysis. Analysing the collected data can identify trends and patterns in employee absences, making it easier to pinpoint areas for improvement that can reduce absenteeism.
You can also evaluate the causes of absenteeism by providing regular anonymous surveys to employees. They allow employees to provide feedback on the workplace morale and culture, workloads, and wellbeing of the workforce, which could be contributing factors in absenteeism.
Just remember that not all employees will be comfortable voicing their opinions, even anonymously, especially if the culture is historically toxic or unsafe for them to do so.
Strategies to reduce the cost of absenteeism
There are a few strategies you can implement to help manage absenteeism costs. The big thing that needs to be done is addressing the causes of absenteeism (surprise, surprise).
Address job-related issues
Maybe you have inadequately trained employees filling roles, and they lack the current capabilities to perform in their role. It’s then about offering stronger onboarding programs and training and development opportunities to build employees’ necessary capabilities to perform their job.
If employees are on top of the capabilities required of them, they’ll be more engaged in the workplace and have greater job satisfaction. This allows them to be a more productive member of the workforce.
We designed Acorn Performance Learning Management System (PLMS) specifically to offer more impactful learning experiences. It’s the only solution that guides learners step by step to master the capabilities of their job roles. By mapping learning content to capabilities, Acorn designs learning pathways that put the right content in front of learners in their moment of need—so they can excel in their role
Implement wellness programs
This is about promoting healthy lifestyles and behaviours to reduce stress and improve mental health and job satisfaction. Some companies offer incentives like gym memberships, counselling or other opportunities to encourage overall health. Health-based job benefits can reduce stress and increase job satisfaction, potentially decreasing absenteeism and fostering a positive and productive workplace culture.
Work-life balance
Employees don’t want to feel that their work is taking over their personal lives. By creating an expectation that work should be kept within business hours (i.e. not expecting employees to work extended hours or over weekends), employees are less likely to experience burnout, stress and overtime fatigue.
Wellness programs also fit in here, by building an expectation that employees have experiences outside the workplace to help them maintain distance between work and home. This allows employees to be more productive and positive members of the workforce, and reduces overtime costs.
Create a positive workplace culture
This is all about preventing toxicity in the workplace and fostering a workplace culture that encourages and engages employees, preventing the occurrence of unexcused absenteeism. This can be done by:
- Encouraging lines of open communication between employees and managers to share feedback and build trust
- Offer flexible work arrangements which allow for a better work-life balance
- Provide support and development opportunities to help engage employees in their work and increase job satisfaction.
- Optimise workloads and job design to reduce stress, burnout, and improve overall job satisfaction.
Key takeaways
The causes of absenteeism vary depending on a number of factors, including the business, industry and time of year. Ergo, your costs of absenteeism also vary.
Absenteeism, when interrogated, can reveal underlying issues in your organisation that make the workplace undesirable for employees, driving up costs, turnover and disengagement while decreasing productivity. Identifying the trends in employee absences allows businesses to improve their workplace and its productivity, improving their bottom line.
Related Reads on This Topic

Strategies & Best Practices to Reduce Your Employee Absence Rate
Absence rates give you insight into employee engagement, job structures and cultural issues that impact productivity and morale…

What is Employee Turnover and How You Can Calculate Your Employee Turnover Rate
Employee turnover is the natural cycle of vacancy and recruitment in a business. But how do you calculate it, and why should you…

How to Benchmark and Calculate Revenue Per Employee
Revenue per employee is the first step to understanding opportunities for improvement in your business. We break down how to calculate RPE…