Learner Engagement: Behavioral, Cognitive, & Affective
Experiencing eLearning
DECEMBER 17, 2019
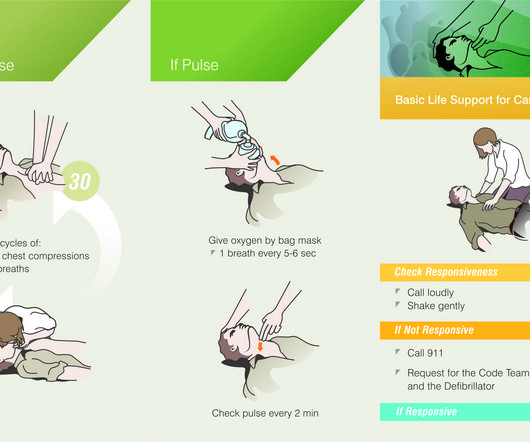
That’s part of behavioral engagement. However, we can also support the cognitive and affective dimensions of engagement. Behavioral engagement. Behavioral engagement is the actions and behaviors people take during learning, which may support or hinder learning. That would be “on-task” behavior.



















































Let's personalize your content